Treatment of asthma
Goals of asthma treatment
Asthma is defined as uncontrolled if you experience discomfort despite following a treatment plan. The overall goal of asthma treatment is therefore to achieve controlled asthma, which means that you can live an active life without limitations, despite your asthma.
Examples of achievable treatment goals:
- To get rid of long-term asthma symptoms that make you less able to cope or sleep worse.
- Not having any problems with asthma in everyday life.
- To reduce the number of asthma attacks.
- To get better quickly if you have an asthma attack.
- That the lungs will function as well as possible in the future.
Different types of treatments
There are different types of treatment for asthma that are used in different combinations depending on how severe the asthma symptoms are.
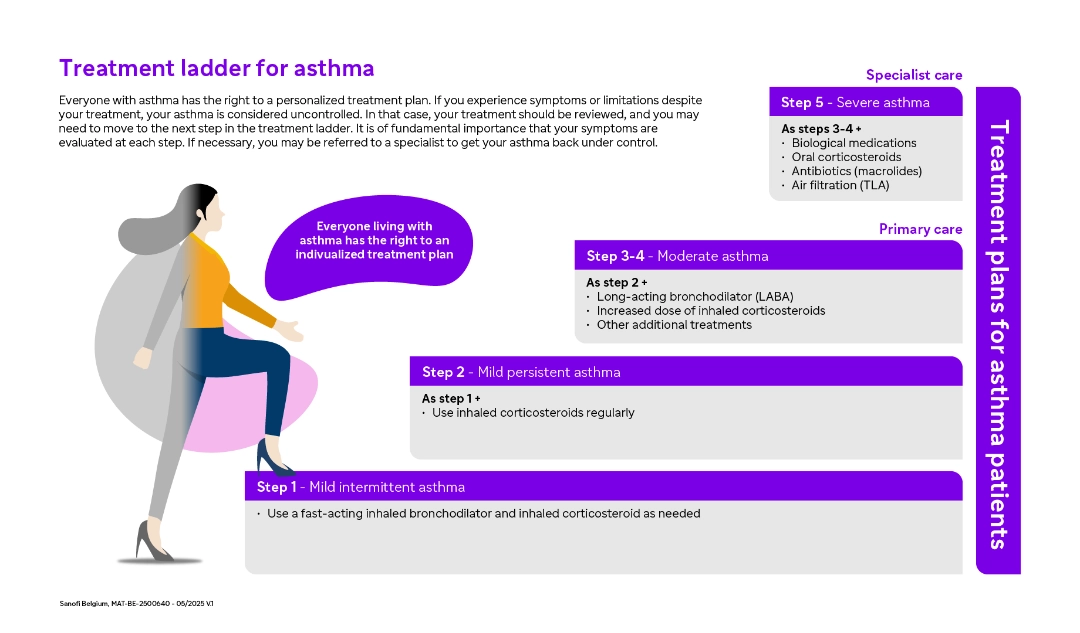
The treatment ladder describes how to medicate different degrees of asthma severity. At each step, an evaluation must be made, to see if the symptoms have improved enough, or if you need to move up to the next step in the treatment ladder. Regular evaluation and referral to a specialist if necessary is important to achieve controlled asthma without symptoms.
Everyone living with asthma has the right to a customized treatment plan with the goal of achieving controlled asthma.
Mild - moderate asthma
- Fast-acting airway dilator inhalation: used to quickly relieve acute asthma symptoms by dilating the bronchial tubes
- Long-acting bronchodilator inhalation: used regularly to keep the bronchial tubes open for a longer period of time, usually up to 12 hours.
- Inhaled cortisone: a preventative treatment that reduces inflammation in the bronchial tubes and is used daily to control asthma symptoms.
Supplements for severe asthma
- Cortisone tablets: used for severe asthma attacks or when asthma cannot be controlled with inhaled medicines. However, cortisone tablets are related to some side effects and should not be used for extended periods of time.
- Biologics: a newer type of treatment that targets specific parts of the immune system to reduce inflammation and improve asthma control.1
- Antibiotics (Macrolides): sometimes used to treat chronic asthma symptoms that are exacerbated by bacterial infections.
- Air filtration (TLA): temperature-controlled laminar airflow (TLA) is used to create a clean air zone around the patient's bed, reducing exposure to allergens and irritants during the night.
Knowing the barriers to asthma control will help you better overcome them
There are a number of barriers that can prevent patients from better controlling their asthma, and each can play a role in addressing this.
- Neglect of symptoms
- Specialist Consultations
- Therapeutic approaches
![]()
Consequences for the individual patient
The symptoms of severe asthma that is not well controlled can be present all the time and affect everyday life both for the person with the disease and those close to them.
![]()
Symptoms
For those with severe uncontrolled asthma, symptoms are part of everyday life, despite many different medications. In addition, they risk life-threatening asthma attacks.2,3
Severe uncontrolled asthma can be recognized by the symptoms, including coughing, wheezing and difficulty breathing. Sleep may be disturbed and opportunities for activities in everyday life limited.
Those living with severe asthma may also need to use emergency medicine in an inhaler for quick relief more than twice a week. In some cases, the daily symptoms may eventually begin to feel normal.
![]()
Society and the economy
The consequences of asthma for society and the economy are often underestimated.
Only 5 to 10 percent of all asthma cases are severe asthma, but they account for 50 percent of the total health care costs of asthma. Asthma is associated with both direct costs, e.g. hospital visits and medicines, and indirect costs, e.g. lost working days or lower productivity.
Long-term use of oral corticosteroids, which is common in severe asthma, can also cause severe side effects, including cataracts, osteoporosis and diabetes.
It is common for severe asthma to go undetected.
The person suffering from severe asthma may not realize the type of asthma they have, and loved ones who do not have asthma may not realize how serious the disease can be. Now that new research is opening up new possibilities for those living with severe asthma, it is more important than ever to increase awareness of the symptoms and how to recognize the disease.
Is your asthma under control?
For millions of people, asthma symptoms are part of everyday life. Many choose to accept the situation as normal. Others think they have their asthma symptoms under control. Are you one of them?
Diagnose and evaluate asthma
Different types of asthma produce different symptoms, and patients experience symptoms and asthma attacks to varying degrees.
- Biologics: Katial RK, et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2017;5:S1–S14
- Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA). Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention. 2018. (http://ginasthma.org/download/832/) (13.02.2020)
- Price D, Fletcher M, van der Molen T. Asthma control and management in 8,000 European patients: the Recognise Asthma and LInk to Symptoms and Experience (REALISE) survey. NPJ Prim Care Respir Med. 2014; 24:14009
Sanofi Belgium, MAT-BE-2500525. V.1. 04/2025